Artificial intelligence (AI) bots now scrape websites to train models and answer questions directly, often without sending traffic back to the original sources. Our new AI audit feature puts control in your hands: you decide which AI bots are allowed on your website – and which aren’t.
The new era of web crawlers
For years, website owners welcomed bots, also known as crawlers, from search engines, as they improved visibility and helped monetize traffic.
AI crawlers are now changing the model. They collect content not just for indexing, but to deliver instant answers directly within AI tools.
For many businesses, this creates new opportunities. Mentions in AI responses can expand reach and attract new audiences.
For others, especially those monetizing through visits, it creates challenges. If an AI tool provides the full answer, only a few readers will click through. No traffic means no income.
Be in charge with AI audit
With AI audit, the choice is yours. Keep the crawlers that bring value. Block the ones that don’t. Adjust your settings anytime.
The feature is available to web hosting and cloud hosting clients using our content delivery network (CDN). You can find it in your website’s dashboard under Performance → CDN → AI Audit.
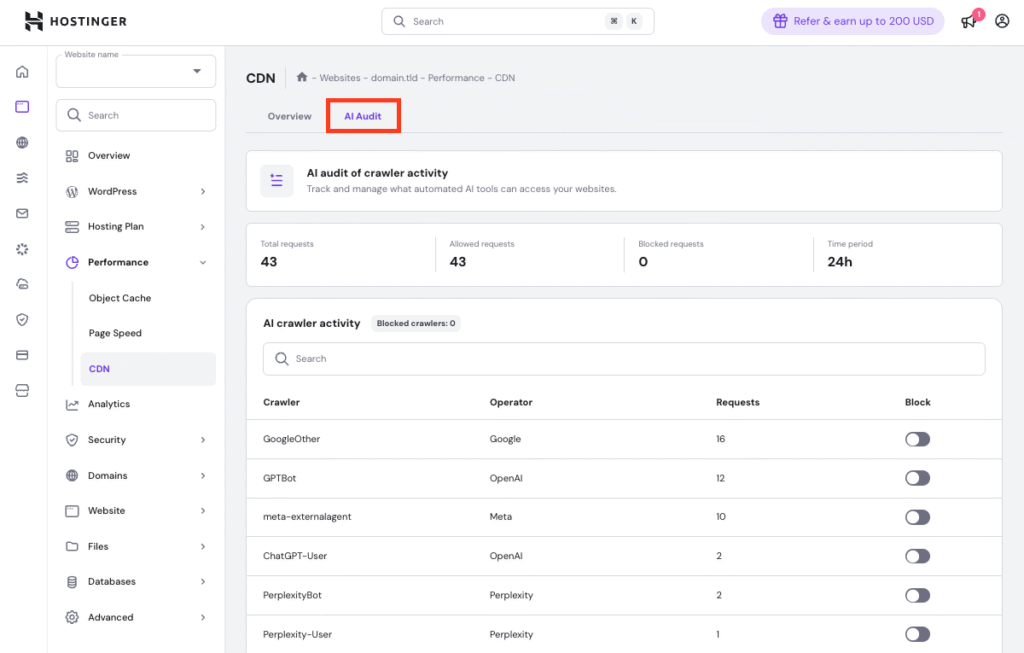
From there, you can:
- See which AI crawlers visit your site
- Track crawler activity and requests over time
- Block the bots you don’t want, while keeping the ones you do
Note: Blocking a crawler prevents future access, but doesn’t erase what it already collected.
Our analysis: How AI bots are crawling the web
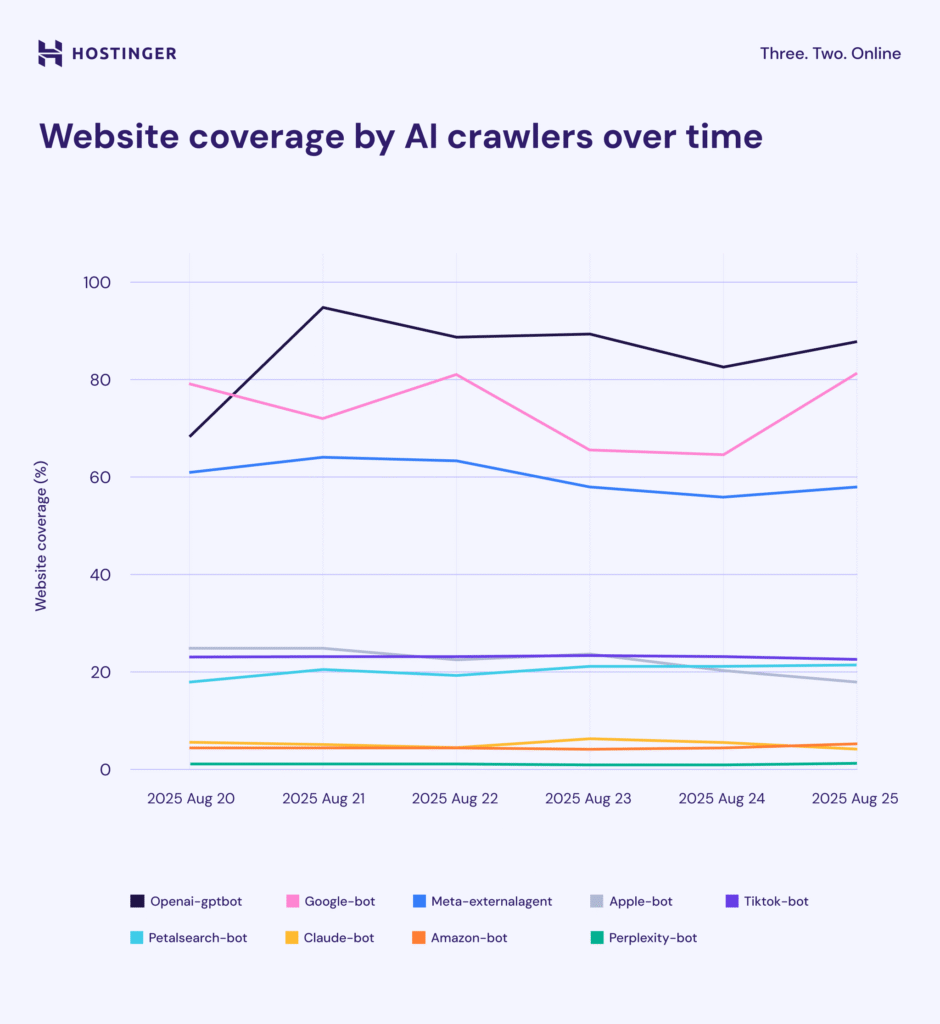
How active are these AI crawlers? To find out, we analyzed logs from 5 million client websites.
Here’s what we discovered:
- Hundreds of crawler groups visit our clients’ websites
- About a third of the most active crawlers are linked to AI providers
- Crawlers from Google, Meta, and OpenAI are the most active, reaching between 60 and 85% of websites daily
- Bots from Apple, ByteDance (TikTok), and Huawei (Petalsearch) typically crawl 20–25% of sites
- Anthropic (Claude), Amazon, and Perplexity, and other AI crawlers visit only 2-5%
Don’t let the lower percentages fool you – crawlers rotate targets and can build a near-complete picture of the web within weeks.
To make crawler activity clearer, here are some examples of common AI bots:
- Amazonbot (Amazon) – Indexes web content for various purposes, including support for Amazon Alexa
- Applebot (Apple) – Crawled data helps power Apple’s features, including the company’s AI assistant Siri
- Openai-GPTBot (OpenAI) – Crawls content that may be used in training generative AI foundation models
- Googlebot (Google) – Google’s main crawler. While its official description doesn’t mention AI training, public data and evidence suggest it may be used for that purpose
- Meta-Externalagent (Meta) – Crawls the web for use cases such as training AI models or improving products
Ready to take control?
The internet is changing fast, but your website is still your space. With AI audit, our CDN extension, you decide who can access your content – aligning visibility with your business goals.
Take control of your content today with the AI audit.
And if you want to increase visibility in AI-generated responses, consider adopting generative engine optimization (GEO) strategies: create well-structured content, improve website loading speed, and add an llms.txt file to make it easier for AI tools to navigate your site.
The post Your website, your rules: Track and control AI bots appeared first on Hostinger Blog.