Artificial intelligence (AI) tools have been part of some workers’ daily routines for a while now. How does AI influence the job market, according to workers in Rhode Island, the smallest state in the United States? Hostinger identified key results from a survey focused on workers’ AI-related fears, and their views on how AI will affect skills, knowledge, advancement, regulation, and the job market generally.
- Clear fear: AI replacing you at work
- Rhode Island workers see value in understanding AI
- Only 3% claim to be experts on AI
- Courage with AI: fears, new skills, and the current moment
- Is AI a positive or negative agent for jobs?
- 53% of workers believe AI is advancing too rapidly
Clear fear: AI replacing you at work
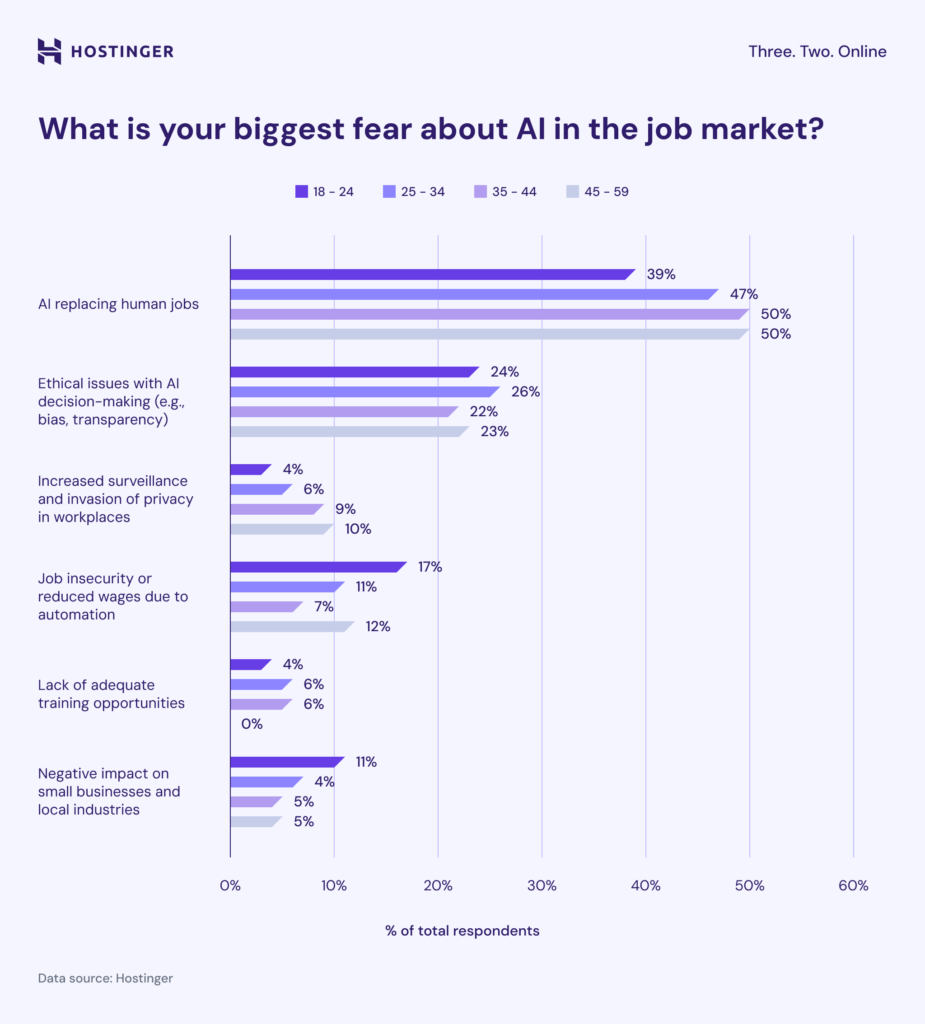
The primary fear revealed in this survey among Rhode Island workers is AI replacing human jobs. 48% of people worry AI technology will replace humans in certain roles. The survey reveals a greater fear among older workers compared to younger ones, in that 50% of workers aged 35-54 view this as a significant concern. However, the numbers are somewhat reduced for Gen Zs (39%) and young adults around 25 to 34 (47%).
Respondents in this New England state are also commonly concerned about ethical issues and reduced wages, factors that ranked second and third, respectively.
Rhode Island workers see value in understanding AI
In Rhode Island, on average, six out of 10 workers agree that they should learn new AI tools and technologies. In education and IT services, that number exceeds 75%, indicating a majority believe in upgrading their AI skills.
Several industries not intrinsically related to tech and digital transformation express doubt about the necessity of adding AI skills to resumes. 47% or less of healthcare, government, and public administration workers say they will consider learning more about it.
Only 3% claim to be experts on AI
Dozens of AI tools are available online, and since OpenAI’s ChatGPT launched in 2022, AI platform use has increased daily. 21% of workers in the Ocean State believe they know more about artificial intelligence than the average person, yet only 3% consider themselves experts in the field. The remaining 76% of respondents claim they know the basics of AI.
Courage with AI: fears, new skills, and the current moment
While Hostinger’s study examined the responses of workers whose primary fear is job loss due to artificial intelligence, data indicates that respondents fearing job loss due to AI are actively adapting in the following ways:
- 54% said they will have to learn new skills because of AI.
- 81% asserted they know the basics, and 17% expressed that they know more than an average person about AI.
Workers with this concern are primarily concentrated in:
- Healthcare (18%)
- Non-profits/social services (14%)
- Education (13%)
- Retail (12%)
“Artificial intelligence changes rapidly. We must remember and trust our ability to adapt to new tools. The user base for AI tools continues to expand, and it is our responsibility to learn and engage in the discussion,” states Eiviltas Paraščiakas from Hostinger.
Is AI a positive or negative agent for jobs?
Opinions on AI’s impact on employment were also examined. Only one out of five respondents believes AI will generate more jobs than it replaces in any state industry. This was consistent across all age groups and most industry backgrounds. An exception is manufacturing workers, 50% of whom expressed a more optimistic view regarding AI’s impact on future job creation.
53% of workers believe AI is advancing too rapidly
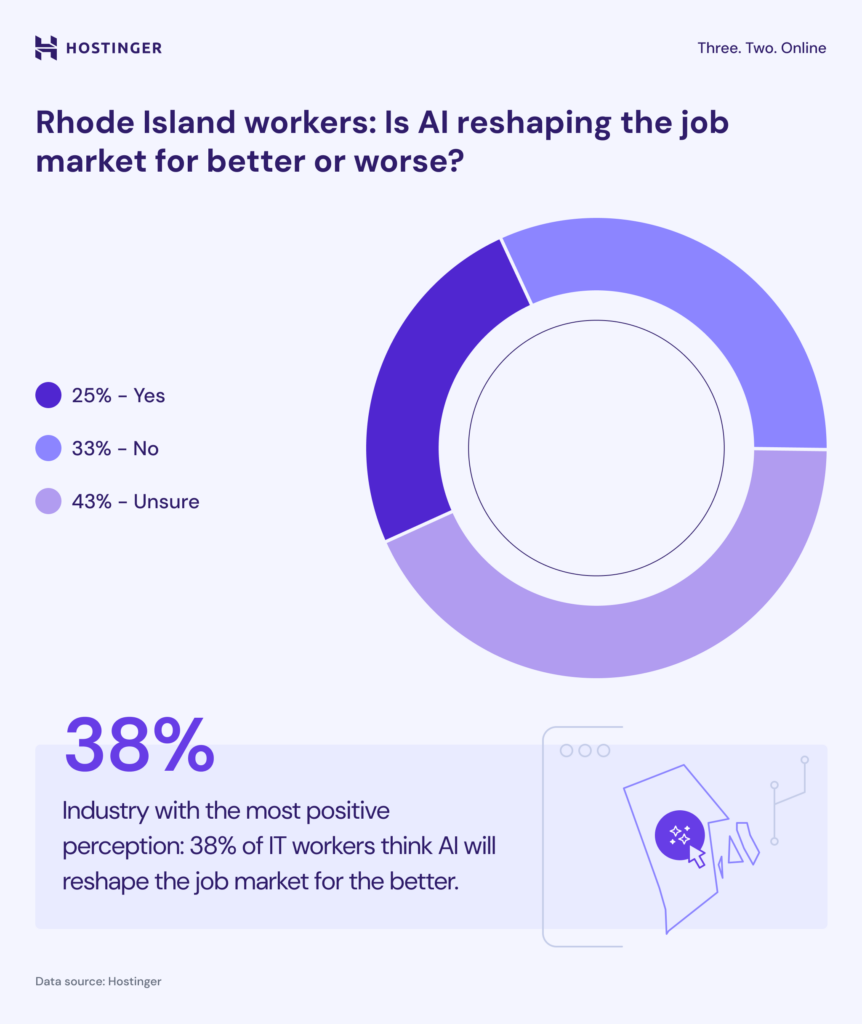
Rhode Island workers view AI’s reshaping of the job market with uncertainty. 53% of respondents believe artificial intelligence is advancing too rapidly for workers to adapt.
Furthermore, when asked about the positive or negative impacts of AI on employment, only 25% said they believe this new technology will create better possibilities for the job market, while 33% predicted a negative impact. The largest group, with 43%, expressed uncertainty.
Overall, it is believed that AI will significantly impact jobs, and that workers’ adaptability will significantly shape the future of most industries. In periods of uncertainty, people’s motivation and perception may slow down or speed up the pace of progress.
Rhode Island’s business and economic environment clearly exemplifies trends in white-collar states. Nearly 60% of the Ocean State’s civilian-employed population is employed in white-collar industries. According to the US Census Bureau, Rhode Island’s employment rate is 61%, and the median household income is $84,900 per year. As the smallest state in the country, Rhode Island’s employment rate and median household income are slightly above the national averages.
Methodology
- The study gathered 300 responses during the first two months of 2025 and is part of the Decoding Trends series of short studies led by Hostinger.
- Take a look at the answers here.
The post Decoding Trends: Rhode Island workers speak on the changes brought by AI appeared first on Hostinger Blog.